
Microsoft has officially introduced the COPILOT function in Excel for Windows and Mac, bringing the power of large language models (LLMs) directly into spreadsheets. This move represents a fundamental shift: AI is now a native feature, not just an external add-in or separate tool. Users can now analyze, summarize, and generate data using natural language prompts directly inside their Excel formulas.
How the COPILOT Function Works
The COPILOT function allows users to enter prompts using natural language in any cell, referencing cell values or ranges as context. The syntax is straightforward:
text=COPILOT(prompt_part1, [context1], [prompt_part2], [context2], …)
Prompt_part: Text that describes the AI’s task (e.g., “Classify this feedback” or “Summarize A1:A50”).
Context (optional): Reference to cells or ranges for the AI to process.

Key Features
Instant AI-Powered Analysis: Input a prompt and context—the function generates summaries, categories, or lists, instantly updating as your data changes.
Seamless Integration: COPILOT sits within Excel’s calculation engine and works alongside standard functions like IF, SWITCH, or LAMBDA, enabling fusion of traditional Excel logic with AI-generated results.
Dynamic Updates: No need to rerun scripts or refresh add-ins. Any change in data automatically recalculates the AI output.
Multiple Use Cases: From sentiment analysis of customer feedback, summary generation, SEO keyword brainstorming, to table/list creation—COPILOT adapts to diverse analytical and creative workflows.
Example Usage
Classifying Feedback: text=COPILOT(“Classify this feedback”, D4:D18)
Generating Lists: text=COPILOT(“Generate airport codes for major US cities”)
Summarizing Data: text=COPILOT(“Summarize”, A1:A50)
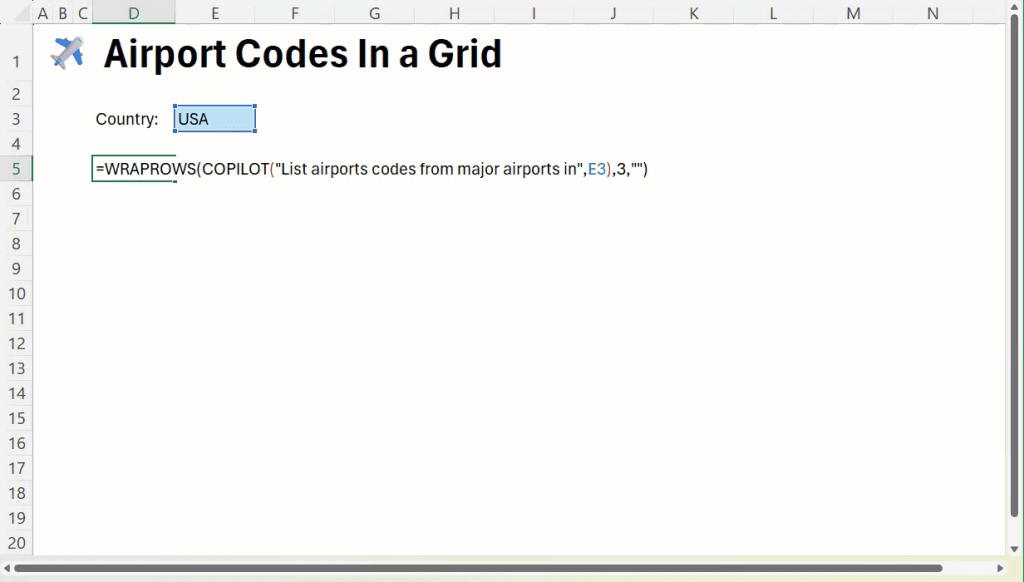

Technical Insights
Auto-Updates & Confidentiality: COPILOT auto-updates with data changes and does not use user-provided data to train the underlying AI models, ensuring confidentiality.
Function Call Limits: Users are permitted 100 calls every 10 minutes and 300 per hour. Passing arrays as a single call can help maximize usage efficiency.
Integration with Existing Functions: COPILOT results can be used as inputs to other formulas, which dramatically expands analytic capabilities within the spreadsheet.
No External Data Access Yet: COPILOT only uses data from within the workbook; support for live web data and internal business docs is planned for future updates.
Optional Implementation: The function is opt-in and only exists in your sheet if you choose to use it.
Availability & Rollout
Beta Channel Users: Available for Microsoft 365 Copilot license holders running Windows Excel version 2509+ or Mac version 16.101+.
Excel for Web: Rolling out soon via the Frontier program.
Comparison to ChatGPT Integration: Unlike external AI chat tools, COPILOT offers native, auto-refreshing analysis—closing the workflow gap for Excel users who previously relied on copy-paste between apps.
Use Case Scenarios
Brainstorming: Quickly generate SEO keywords, rewrite messaging, or ideate product features.
Classification & Tagging: Categorize support tickets, survey responses, or feedback at scale—no need for external tagging tools.
Reporting & Summarization: Turn complex datasets into digestible narratives for stakeholders.
Automation: Build lists, tables, and project plans with a single prompt, instantly populating the grid.
Tips for Using COPILOT
Prompt Engineering: Clarity matters—give explicit instructions, specify ranges, and set desired output formats (e.g., tables, lists).
Directives: Use action-oriented instructions (“summarize”, “categorize”) for better results.
Validation: Always review AI-generated outputs, especially for business-critical tasks.
Usage Strategy: Maximize calls by referencing arrays versus individual cells.
Conclusion
The COPILOT function marks a pivotal moment for Excel, embedding advanced AI directly into the most widely used analytics platform in business. With the ability to generate, analyze, and summarize data natively, Excel is transforming how users interact with their data—making workflows smarter and more efficient. The native integration bridges the gap between spreadsheet and AI, and signals a future where generative models become default companions in business analytics.
Check out the Technical details. Feel free to check out our GitHub Page for Tutorials, Codes and Notebooks. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.

Michal Sutter is a data science professional with a Master of Science in Data Science from the University of Padova. With a solid foundation in statistical analysis, machine learning, and data engineering, Michal excels at transforming complex datasets into actionable insights.
